What is Groove Bearing and How Does It Work?
Groove bearings play a vital role in various mechanical systems. These components allow for smooth rotational movement while supporting heavy loads. As noted by industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, "Groove bearings are essential for enhancing the efficiency of machinery."
In practice, groove bearings can be found in applications ranging from automotive engines to industrial machinery. They consist of a cylindrical surface that offers precise alignment and stability. However, despite their advantages, these bearings can wear over time, necessitating regular checks and maintenance.
Understanding how groove bearings operate can help in identifying potential issues early on. Regular inspections are crucial, yet many overlook this practice. Failing to maintain groove bearings can lead to severe machinery breakdowns. Simple actions can prevent costly repairs and ensure optimal performance.
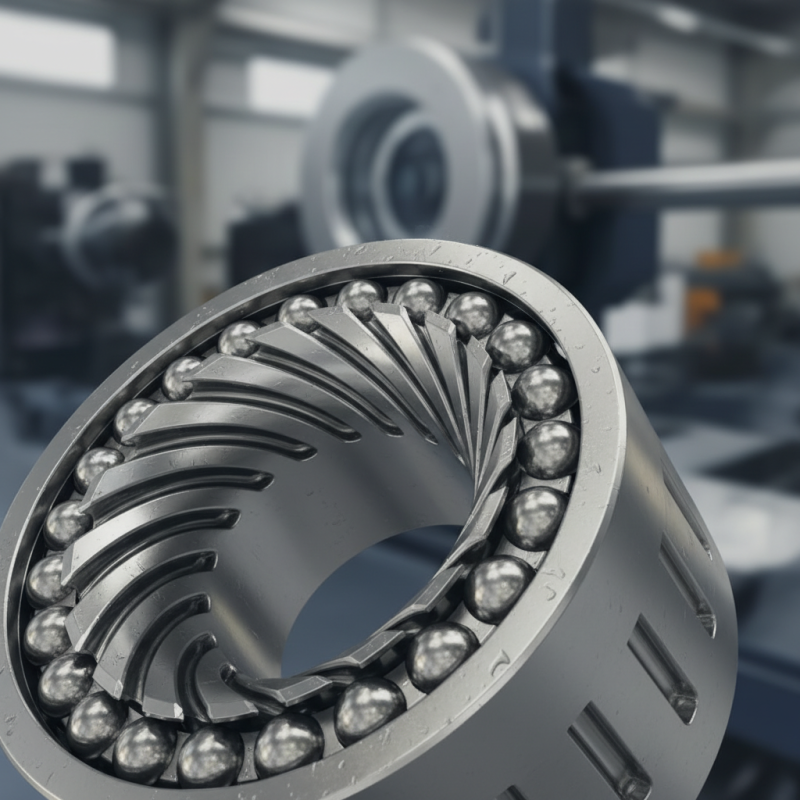

What is a Groove Bearing?
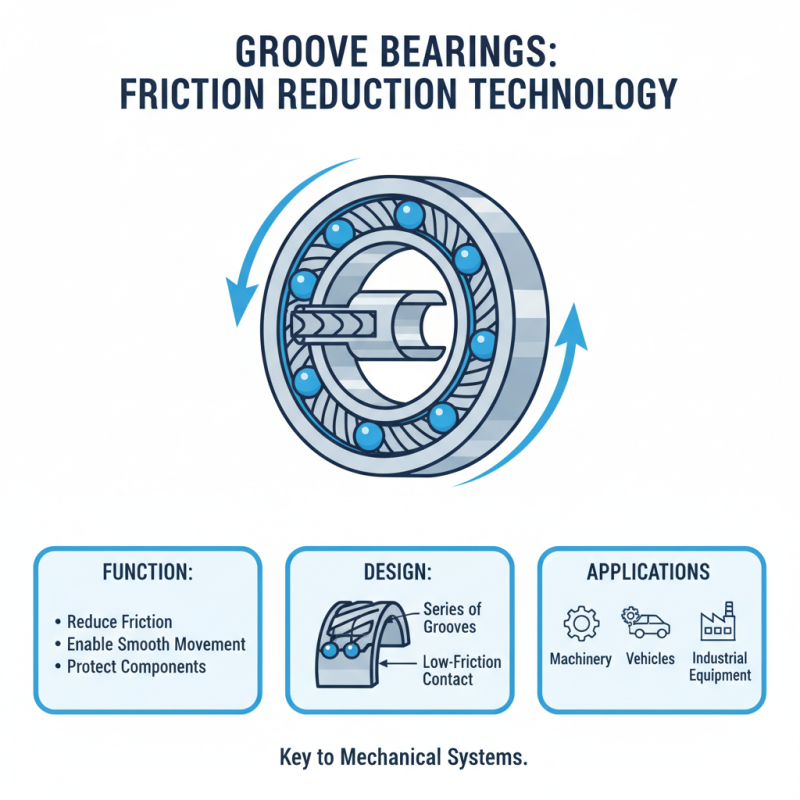
Groove bearings play a crucial role in various mechanical systems. They are designed with a series of grooves that help reduce friction between moving parts. This design allows for smooth movement of shafts and other components. They are commonly used in machinery, vehicles, and industrial equipment.
The grooves in the bearing provide channels for lubricant. This helps in minimizing wear and tear. The design aids in distributing load evenly over the bearing surface. However, manufacturing quality can vary. Sometimes the grooves may not be perfectly aligned. This misalignment can lead to performance issues and increased friction. Users must ensure proper installation and maintenance.
Understanding the working principle of groove bearings is essential. They operate on the basic principle of reducing friction. The smooth interaction between surfaces allows for enhanced efficiency. Yet, users should regularly check for signs of wear. Neglecting maintenance can lead to unexpected failures. Each component in a system must work together harmoniously for optimum performance.
The Structure and Components of Groove Bearings
Groove bearings are critical components used in various mechanical systems. Their design includes a cylindrical groove, which helps in reducing friction. This feature allows smoother operation when two surfaces move against each other. Groove bearings come in different sizes and materials. Their structure generally includes the outer race, inner race, and the rolling elements. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring efficient motion.
The materials used often impact performance. Steel and ceramic are common, each offering unique advantages. A report from the Machinery Components Network highlights that ceramic bearings can withstand higher loads than steel. They also resist wear better. However, ceramic materials can be brittle and may require careful handling.
**Tip:** When selecting groove bearings, consider the weight and speed of your application. Choosing the wrong material can lead to premature failure.
Manufacturers continuously improve groove bearing designs. New technologies are being explored. For example, hybrid bearings combine materials to maximize strength and reduce friction. However, these advancements come with a cost. Some users may find the pricing of high-tech solutions prohibitive. This can lead to a misjudgment about long-term savings versus initial costs.
**Tip:** Always weigh the benefits of technology against your budget constraints. Quality cannot be compromised for the sake of costs.
Groove Bearing Performance Characteristics
How Groove Bearings Function in Mechanical Systems
Groove bearings play a significant role in the smooth operation of various mechanical systems. These bearings are designed with grooves that help reduce friction and allow for better lubrication. This unique design is essential in applications like robotics, automotive, and industrial machinery. According to a report by the Industrial Bearings Market, the use of groove bearings is projected to grow by 5% annually.
In mechanical systems, groove bearings function by distributing the load evenly across the bearing surface. This design minimizes wear and tear, which can lead to system failures. Reports indicate that improper bearing installation contributes to approximately 30% of machinery breakdowns. Ensuring correct alignment and lubrication is vital for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of groove bearings.
While their benefits are clear, challenges persist. Over time, contaminants can accumulate in the grooves, causing performance issues. Regular maintenance is necessary to address this, but it is often overlooked. The industry must focus more on training personnel for better maintenance practices. Improved awareness could potentially cut down on operational costs by 15%, as highlighted by recent mechanical engineering studies.
Applications of Groove Bearings in Various Industries
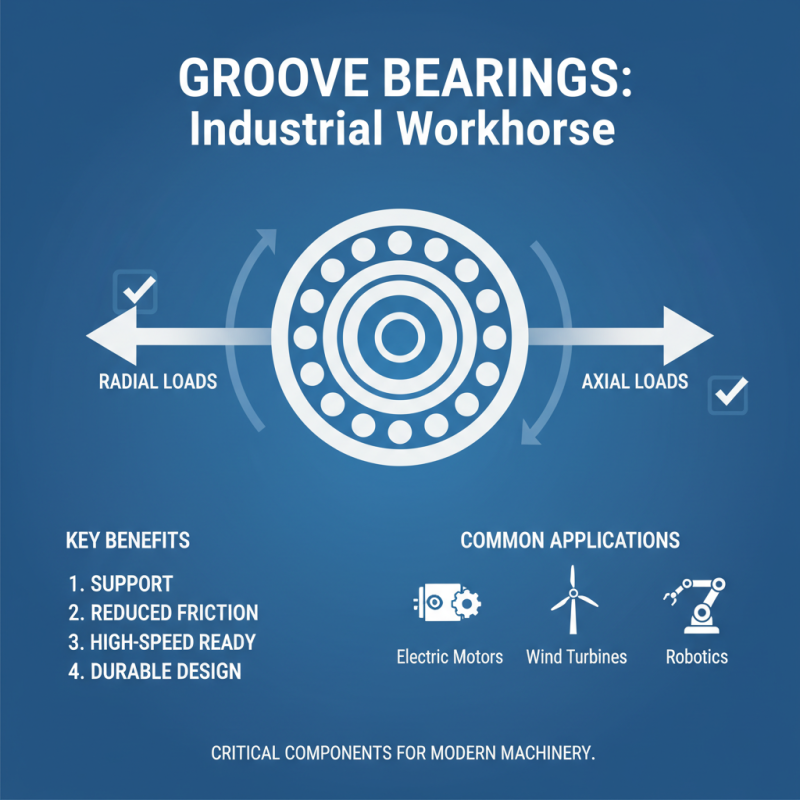
Groove bearings are critical components in many industries. They provide support and reduce friction in various mechanical systems. Their unique design allows them to handle radial and axial loads effectively. This capacity makes them popular in high-speed applications, such as electric motors.
In the automotive sector, groove bearings support rotating shafts in engines. They ensure smooth operation and reliability. In construction equipment, these bearings help heavy machinery function correctly under extreme conditions. Their durability is crucial for maintaining performance over time.
The aerospace industry also benefits significantly from groove bearings. These components must operate safely at high speeds and speeds. However, the research on material selection for these bearings is ongoing. There are still challenges to address regarding weight reduction and performance efficiency. Continuous improvement is necessary to enhance their capabilities further.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Groove Bearings
Groove bearings offer distinct advantages in various industrial applications. One key benefit is their ability to reduce friction. This characteristic can lead to lower energy consumption, which is crucial in today’s energy-conscious environment. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, friction reduction technologies can improve efficiency by up to 30% in certain machinery. This is a significant figure for manufacturers looking to optimize production costs.
However, groove bearings do come with limitations. Their design may restrict certain movements, which could impact performance in complex systems. For example, in environments with heavy loads, wear and tear can occur more rapidly. A study from Machinery Lubrication highlights that nearly 40% of bearing failures arise from improper load distributions. This emphasizes the need for careful design and application assessment.
Moreover, while groove bearings are beneficial, they may require specific lubrication methods. Maintenance can become complex without regular checks. Data from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers indicates that maintenance errors account for approximately 25% of bearing failures. Thus, while groove bearings can enhance efficiency, they necessitate diligent oversight to avoid potential drawbacks.
Related Posts
-

The Future of Groove Bearings in Sustainable Engineering Solutions
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using Groove Bearings in Industrial Applications?
-

Understanding Groove Bearings: Essential Insights for Enhanced Mechanical Efficiency
-

7 Essential Tips for Choosing the Best Pillar Bearing for Your Needs
-

Top 10 Deep Bearing Types for Optimal Performance in Various Applications
-

10 Facts About Real Bearing for Optimal Performance in Your Machinery